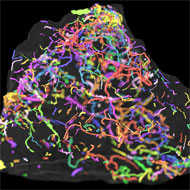
Fossil discovery sheds new light on animal evolution
Newly discovered fossils could alter the way we think about how animals evolved on earth, scientists say.
An international team found a new set of trace fossils - tracks and burrows left by living organisms - that were left by some of the first organisms capable of active movement.
The fossils date back to the period known as the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition around half a billion years ago. In context, dinosaurs lived in the Mesozoic Era, between 230 and 65 million years ago.
This is significant because the trace fossils pre-date similar animals found in the fossil record.
Dr Russell Garwood from the University of Manchester explained: “These fossils are found in rock layers which actually pre-date the oldest fossils of complex animals - at least that is what all current fossil records would suggest.”
They were found in sediment in the Corumbá region of western Brazil. The creatures that made these burrows were about the size of a human hair, measuring from under 50-600 micrometers in diameter. Scientists believe they were ‘nematoid-like’ organisms similar to a modern-day roundworm.
Lead author Luke Parry, from the University of Bristol, added: “Our new fossils show that complex animals with muscle control were around approximately 550 million years ago, and they may have been overlooked previously because they are so tiny.”
The animals that made the fossils are bilaterians, which are more complex and much more closely related to humans than simple creatures such as jellyfish.
Parry added: “Most fossils of bilaterian animals are younger, first appearing in the Cambrian period.”
In order to find the tiny fossils, scientists used x-ray microtomography, which creates a virtual, 3D model of something without destroying the original object. This could offer an unexplored method of tracking animal evolution in deep time.
Image courtesy of the University of Manchester



 The veterinary mental health charity Vetlife is inviting the veterinary community to join it for a sponsored cold-water dip.
The veterinary mental health charity Vetlife is inviting the veterinary community to join it for a sponsored cold-water dip.