Experts assess likelihood of disease entering primate populations
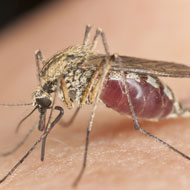
The Zika virus could be transmitted to primates in areas where Zika infections are prevalent, a leading expert has warned.
According to ScienceNews, disease ecologist Barbara Han said that if Zika spreads to primates, the animals could serve as a reservoir for human outbreaks.
This would make it almost impossible to get rid of the virus, she cautioned.
Ms Han was speaking at the American Society for Microbiology Biothreats meeting, which took place in Washington (6-8 February). She and her colleagues assessed the likelihood of Zika entering primate populations in South America using criteria such as body size, diet and species range.
On their list of at-risk species is the black-striped capuchin monkey and the common marmoset - both of which have already tested positive for Zika virus matching the human strain.
‘The finding indicates the spill-back has already started,’ reports ScienceNews.
Capuchin monkeys are particularly at risk, experts say, due to their close proximity with humans.
Zika is spread by the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito and can be passed from a pregnant women to her foetus. Infections during pregnancy can lead to serious birth defects, such as an abnormally small head.
In November, the World Health Organisation declared that Zika was no longer a global emergency. However, Zika virus and its associated consequences still remain a significant challenge to public health.



 The Animal and Plant Health Agency (APHA) has updated its online reporting service for dead wild birds.
The Animal and Plant Health Agency (APHA) has updated its online reporting service for dead wild birds.