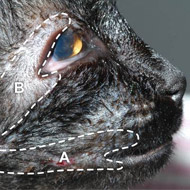
Billie suffered from eyelid agenesis
US vets have been able to create new eyelids for a cat by transplanting tissue from her cheek and lips.
Nine-month-old Billie, a female domestic shorthair, was born without the upper part of her eyelids - a condition known as eyelid agenesis.
The condition meant that Billie was unable to close her eyes completely and the hair in that area rubbed on her cornea, irritating and inflaming her eyes.
An examination by ophthalmologists at the UC Davis Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital revealed that she did not have any scratches on the cornea or inflammation inside the eye. However, the eyelid agenesis was extensive and had resulted in chronic irritation to the surface of both eyes.
Not only this, Billie's vision was impaired due to other birth defects that subtly affected the back of her eyes. Her light perception was good though, and responded to gestures towards the eye, indicating that the remaining vision was worth saving.
Based on the examination, the ophthalmologists thought Billie would be a good candidate for a corrective surgery that had been performed elsewhere over the past five years, but never at UC Davis.
Following a paper published in 2010, which described groundbreaking surgery to correct ageneses, members of the Opthalmology Service began practising the transplant technique, which involved removing tissue from the cat's cheek and lips and transplanting it as an eyelid.
After several successful trials, the team discussed the procedure with the cat's owner, who agreed to the surgery. Known as a lip commissure to eyelid transposition, the surgery on Billie was a success.
Since Billie’s surgery, UC Davis has performed two other lip commissure to eyelid transpositions, both of which were also a success.



 The Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) is inviting applications from veterinary students to attend a one-week extramural studies (EMS) placement in July 2026.
The Veterinary Medicines Directorate (VMD) is inviting applications from veterinary students to attend a one-week extramural studies (EMS) placement in July 2026.