Simple blood test could allow for the early detection of the disease
One of the UK’s native gun dogs, the flat-coated retriever, is set to benefit from new research into a rare but aggressive form of cancer.
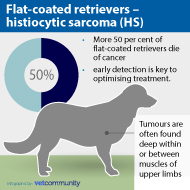
Research shows more than 50 per cent of flat-coated retrievers die of cancer and the breed is particularly susceptible to histiocytic sarcoma (HS) - a type of cancer found in multiple locations across the body. The outlook for the disease is extremely poor and, in most cases, terminal.
Now scientists at the Animal Health Trust (AHT) and the University of Cambridge are set to carry out new research into the creation of a blood test for the early detection of HS in flat-coated retrievers. An early diagnosis would improve the chances of successful treatment and extend survival time.
Dr Anna Hollis, a cancer researcher at the AHT, said: “I have flat-coated retrievers and have lost one of them to histiocytic sarcoma - it is absolutely devastating. This research could make a significant difference, and that is a huge personal motivation for me."
In the study, researchers plan to confirm if there is a specific microRNA ‘signature’ that is unique to HS amongst tumours and tissue samples from flat-coated retrievers. MicroRNAs are often found in tumours and vary between different types of cancer.
If such a signature is identified, the project will investigate if measuring the levels of these microRNAs within a flat-coated retriever tissue sample can be used to identify a histiocytic sarcoma.
Should the team identify a microRNA ‘signature’ in histiocytic tumours, they will then seek additional funding to see if the same signature can be identified in the blood of affected dogs. If they find a microRNA signature, this could potentially be identified by a single blood test.
This would mean that a blood sample from a flat-coated retriever that was lame could be tested for the presence of HS-associated microRNAs - allowing for the disease to be detected at an earlier stage.
Dr Hollis continued: “Often lame dogs are rested and given pain relief before imaging is sought. Delayed diagnosis is a potential problem with histiocytic sarcoma given its aggressive nature and ability to spread rapidly to other locations within the body.
"If we could identify affected dogs at an earlier stage, this may allow more successful treatment of the disease.”



 HMRC has invited feedback to its communications regarding the employment status of locum vets and vet nurses.
HMRC has invited feedback to its communications regarding the employment status of locum vets and vet nurses.