A warm, wet autumn could lead to a significant rise in cases
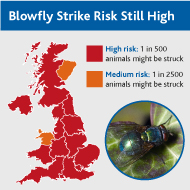
Blowfly strike risk remains “high” across much of the UK, according to the latest update from Elanco and the National Animal Disease Information Service.
The report shows that while a couple of areas have been downgraded to “Medium” (North Wales and East Scotland), the high blowfly population remains a threat.
“This is probably the most difficult period to accurately forecast blowfly strike risk during the year because although fly populations remain high, egg-laying and maggot survival are highly dependent on the weather,” explained Richard Wall, professor of zoology and compiler of the Blowfly Risk Alerts.
“If it remains warm through September, risk will remain high, and because many of the treatments applied in early Summer are approaching the end of their period of residual protection, a warm wet autumn can lead to a big increase in strike cases.”
He continued: “The strike risk should still be viewed as 'high' throughout most lowland areas of the UK, but with appropriate note taken of the changing weather."
A study by Elanco and the National Farm Research Unit found that 99 per cent of farmers have suffered financial losses as a result of blowfly strike. A further 82 per cent agreed that the blowfly season is getting longer, with cases of strike being reported as early as February and as late as November.
The consequences of blowfly strike can be devastating, leading to welfare problems and production losses. Figures show it can cost up to £200 to breed a replacement ewe and as much as £80 loss per lamb per death.
Farmers and health professionals seeking to guard against blowfly this year can view real-time map reports at farmanimalhealth.co.uk.



 The veterinary mental health charity Vetlife is inviting the veterinary community to join it for a sponsored cold-water dip.
The veterinary mental health charity Vetlife is inviting the veterinary community to join it for a sponsored cold-water dip.